Polyphenols are a diverse group of naturally occurring compounds found in plant-based foods and beverages, including fruits, vegetables, tea, coffee,...
Most of us think of bacteria making up the entire human microbiota, but there are other key players as summarized below: Bacteria: Bacteria...
In recent years, the field of microbiome testing has gained significant attention as a powerful tool for understanding the complex...
In the world of nutrition, few nutrients hold as much importance as dietary fiber. While often overlooked, fiber plays a...
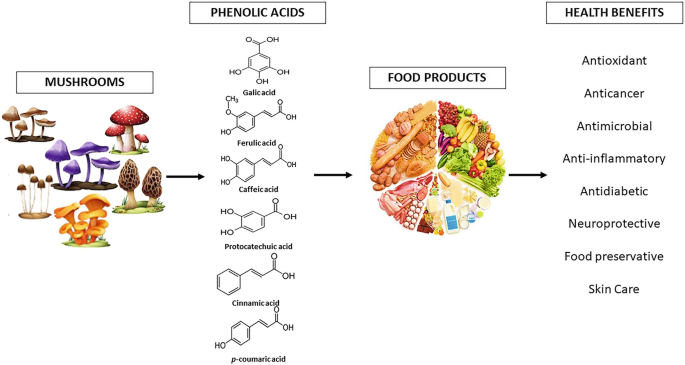
Agaricus blazeii Murill, also known as Himematsutake or Royal Sun Agaricus, is a fascinating mushroom that boasts a rich history...
Maintaining a healthy gut involves more than just probiotics – prebiotics play a crucial role too. Prebiotics are dietary fibers...
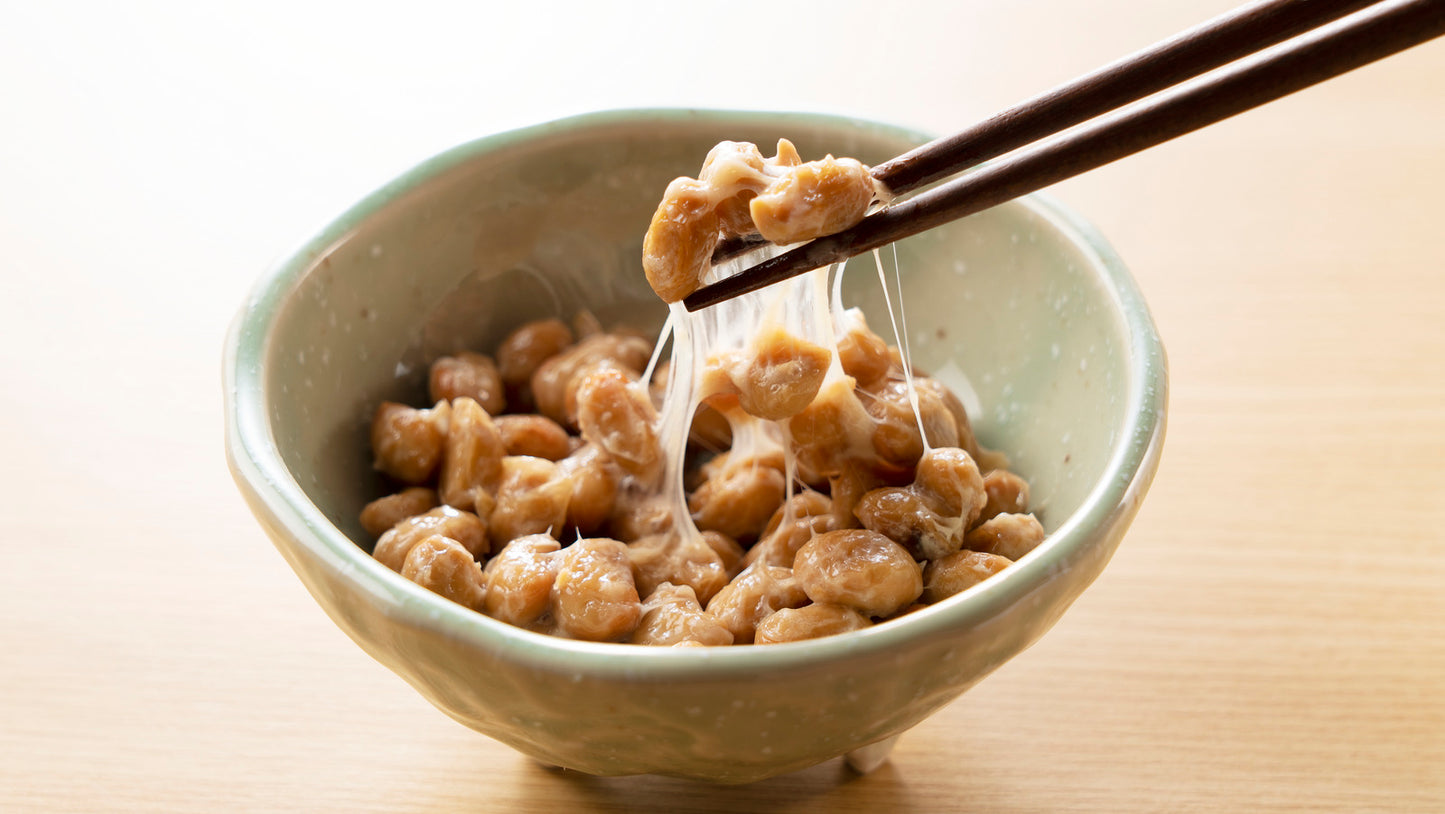
In the far-reaching corners of ancient Japan, there was a dish that held both mystery and fascination - Natto. Its...